Ketamine medication, also known as “Special K,” is a powerful dissociative anesthetic recently gaining popularity for its recreational use. However, Ketamine is not just a party drug but also an essential medication used in medical settings for anesthesia and pain management. The global need for Ketamine is significant, as it is listed on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines.
This blog will discuss how long Ketamine can be detected in saliva, blood, urine, hair, and breast milk after use. It will also cover factors impacting detection time, the duration of Ketamine’s effects, and the experience of Ketamine withdrawal.
In this blog
ToggleWhat Is the Half-Life of Ketamine?
When we talk about the half-life of a drug, we mean the time it takes for the amount of the drug in your body to be reduced by half. The amount of time it takes for Ketamine’s half-life can vary due to different factors. Typically, Ketamine has a half-life of about 2 to 3 hours. This means that after 2 to 3 hours, half of the Ketamine in your body will have been removed.
Factors Affecting Ketamine Elimination from the Body
Several factors can affect the elimination of Ketamine from the body. These factors include metabolism, age, body weight, and liver and kidney function.
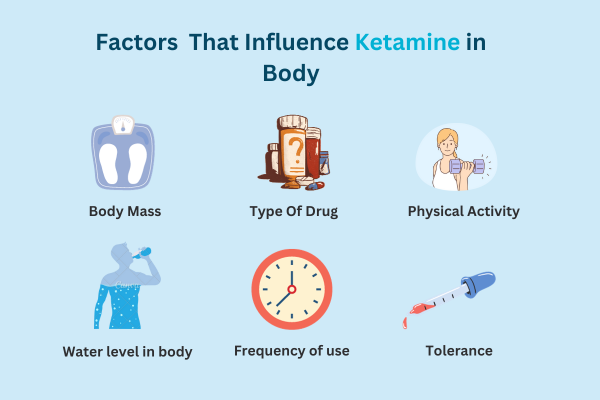
Metabolism is crucial in how quickly Ketamine is broken down and eliminated from the body. Individuals with a faster metabolism may eliminate Ketamine more rapidly than those with a slower metabolism.
Age can also impact the elimination of Ketamine. Younger individuals tend to have a faster metabolism and may eliminate Ketamine more quickly than older individuals.
Body weight is another factor affecting how long Ketamine stays in the body. Individuals with a higher body weight may eliminate Ketamine more slowly than those with a lower body weight.
Liver and kidney function are essential for eliminating drugs from the body. If an individual has impaired liver or kidney function, it may take longer for Ketamine to be eliminated.
How Long Does Ketamine Stay in Your System?
The duration that Ketamine stays in the body differs for everyone and depends on various factors. These factors include the amount taken, how often it’s used, metabolism, and the type of drug test used. Here’s a simple guide to how long Ketamine could be detected in different drug tests:
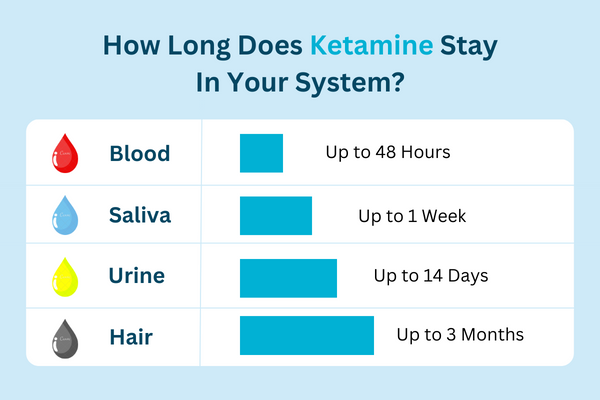
How Long Does Ketamine Stay in Blood?
Similar to urine, Ketamine can also be detected in blood for a certain period of time after use. The detection time in blood can vary depending on factors such as the dose and frequency of Ketamine use.
Ketamine can be detected in blood for up to 1 to 3 days after use. However, in heavy or chronic users, Ketamine can be seen in blood for up to 7 to 10 days.
Factors that can affect the detection time of Ketamine in the blood include the individual’s metabolism, liver function, and the sensitivity of the drug test being used.
How Long Does Ketamine Stay in Saliva?
Ketamine can also be detected in saliva for a certain period of time after use. The detection time in saliva can vary depending on the dose and frequency of Ketamine use.
Ketamine can be detected in saliva for up to 1 to 3 days after use. However, in heavy or chronic users, Ketamine can be seen in saliva for up to 7 to 10 days.
Factors that can affect the detection time of Ketamine in saliva include the individual’s metabolism, hydration levels, and the sensitivity of the drug test being used.
How Long Does Ketamine Stay in Urine?
Ketamine can be detected in urine for a certain period of time after use. The detection time in urine can vary depending on several factors, including the frequency and amount of Ketamine used.
Ketamine can be detected in urine for up to 2 to 4 days after use. However, in heavy or chronic users, Ketamine can be seen in urine for up to 7 to 14 days.
Factors that can affect the detection time of Ketamine in urine include the individual’s metabolism, hydration levels, and the sensitivity of the drug test being used.
How Long Does Ketamine Stay in Hair?
Ketamine can also be detected in hair follicles for an extended period of time after use. The detection time in hair can vary depending on factors such as the length of hair and the frequency of Ketamine use.
Oetamine can be detected in hair for up to 90 days after use. However, it is essential to note that hair tests are not as commonly used as urine or blood tests for detecting Ketamine use.
Factors that can affect the detection time of Ketamine in hair include the length of hair and the frequency of Ketamine use.
How Long Does Ketamine Stay in Breast Milk?
Ketamine’s presence in breast milk can raise concerns for breastfeeding mothers. Similar to its detection in saliva, the duration ketamine remains in breast milk can vary depending on various factors.
Ketamine can be detected in breast milk for up to 1 to 3 days after use. However, in individuals who are heavy or chronic users of Ketamine, it may be detectable in breast milk for up to 7 to 10 days.
Several factors influence the detection time of Ketamine in breast milk, including the individual’s metabolism, the amount and frequency of ketamine use, and other physiological factors. It’s important to note that eliminating Ketamine can vary from person to person.
Ketamine Tolerance and Dependence
Tolerance refers to the body’s reduced response to a drug over time, requiring higher doses to achieve the same effects. On the other hand, dependence is when the body relies on a medication to function normally.
With Ketamine use, tolerance and dependence can develop over time. Regular use of Ketamine can lead to the body adapting to its effects, resulting in the need for higher doses to achieve the desired outcomes.
Dependence on Ketamine can also develop, leading to withdrawal symptoms when the drug is stopped. These withdrawal symptoms can include cravings, anxiety, depression, and difficulty sleeping.
Risks and Side Effects of Ketamine Use
While Ketamine has legitimate medical uses, its recreational use has various risks and side effects. Short-term hazards of Ketamine use include confusion, hallucinations, and impaired coordination. In higher doses, Ketamine can cause a state known as “K-hole,” where individuals may experience a complete dissociation from their surroundings.
Long-term risks of Ketamine use include bladder and kidney damage and cognitive impairments. Chronic use of Ketamine can lead to a condition known as “Ketamine bladder syndrome,” characterized by urinary frequency, urgency, and pain.
Common side effects of Ketamine use include nausea, vomiting, and dizziness. In some cases, individuals may also experience a rapid heartbeat and high blood pressure.
Ketamine Withdrawal symptoms?
Ketamine withdrawal is characterized by symptoms that can emerge when individuals cease or reduce their drug use. These symptoms may include intense cravings, mood swings, fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and physical discomfort like muscle aches and nausea.
Managing ketamine withdrawal is essential, and seeking professional help is strongly advised to receive guidance, symptom management, and effective coping strategies. Professional support can be instrumental in reducing the risk of relapse and ensuring a smoother transition toward recovery for those dealing with ketamine dependence or withdrawal.
Ketamine detox
Ketamine detox refers to the process of safely and systematically discontinuing the use of Ketamine while managing and alleviating withdrawal symptoms. Detoxification from Ketamine is typically the first step toward recovery from ketamine dependence or addiction.
During a ketamine detox program, individuals may receive medical supervision and support to ensure Safety and comfort throughout the withdrawal process. Healthcare professionals may use various strategies to help manage withdrawal symptoms, including medications when necessary. The duration and intensity of ketamine detox can vary depending on the individual’s level of dependence and the specific treatment approach chosen. After completing detox, individuals often proceed to additional treatment modalities, such as therapy and counseling, to address the underlying factors contributing to their ketamine use and to develop skills for long-term recovery. Detox alone is typically insufficient for sustained recovery, and ongoing support is crucial. If you or someone you know needs a ketamine detox program, it is advisable to seek guidance and assistance from a healthcare provider or addiction specialist to create a tailored plan for recovery.
Seeking Help for Ketamine Addiction
It is crucial for individuals struggling with Ketamine addiction to seek help. Ketamine addiction can severely affect physical and mental health, relationships, and well-being.
There are various resources available for individuals seeking help for Ketamine addiction. These resources include addiction treatment centers, support groups, and counseling services. It is essential to reach out to professionals who can provide guidance and support throughout the recovery process.
Final Words From AzDrug
In conclusion, Ketamine is a powerful drug with both medical and recreational uses. Understanding the half-life of Ketamine and the factors that affect its elimination from the body is essential for individuals using or testing for the drug.
Ketamine can be detected in urine, blood, hair, and saliva for varying periods depending on factors such as frequency of use and individual characteristics. It is important to note that Ketamine use comes with risks and side effects, and seeking help for addiction is crucial for those struggling with its use.
Overall, Ketamine is a complex drug that requires careful consideration and responsible use.